When OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022, it sent shockwaves through the tech industry specifically and the whole world at large. For the period after through early 2023, as ChatGPT took over daily conversations, everyone wondered “Where’s Google?” It seemed like Google, which everyone believed would bring AI, was being left behind in this burgeoning field. Well, things have changed now. Google, far from conceding defeat, has quietly and strategically rebuilt its AI capabilities, culminating in the release of Gemini in December 2023. But first let’s build the context.
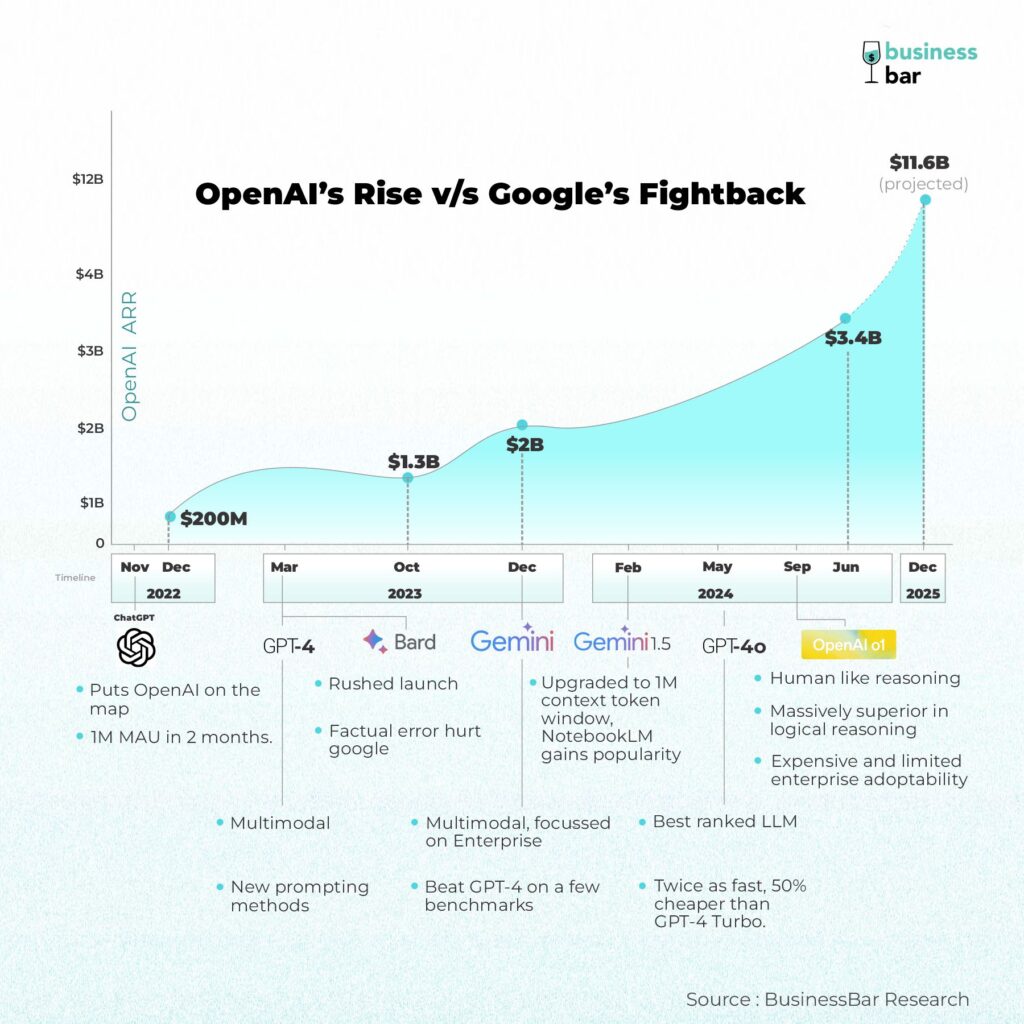
OpenAI beat Google in launching a consumer AI app and took the world by storm. Capturing public imagination with 100M MAU in 2 months and setting off a frantic race among tech-giants, startups and VCs alike. Google’s initial response, Bard, launched in March 2023, was rushed and an underwhelming attempt to catch up. A factual error during Bard’s initial demo cost Google dearly, wiping out roughly $100Bn in market value and much more in reputational damage.
Microsoft’s Open – AI Hedge
Ironically, Microsoft had earlier invested $1Bn in OpenAI in 2019 under the radar, fearing it was years behind Google in its AI research and infrastructure led by its CTO Kevin Scott. But that was now hailed as the futuristic vision of Satya Nadella. It later went on to invest a total of $13Bn into OpenAI valuing it at $80Bn, along with the biggest investors of the valley, Thrive Capital, Sequoia Capital, and a16z.
OpenAI is in talks to close a $6.5B funding round soon valuing it at $150B. This would almost confirm the rumors of it converting to a for-profit company and a 7% equity stake for Sam Altman. OpenAI is expected to lose $5B this year. There is also some trouble brewing at OpenAI following the abrupt exit of its CTO Mira Murati. More on this later [Update: In the process of publishing this, OpenAI closed its round at $6.6Bn valuing it at $157B ]
Microsoft became the exclusive cloud provider for OpenAI and started integrating OpenAI models into Azure, Github Co-pilot and its Office suite to bring in larger enterprise sales. Through 2023, Azure revenues grew over 30%, with even higher growth projected, it caught up to AWS, and became the world’s most valued company nearly doubling its market cap to $3Tn since the start of 2023 It seemed like a great match that dramatically altered the company’s fortunes in AI.
Projected to earn $1Bn by 2024, ChatGPT achieved a $1.6Bn ARR by the end of 2023 and doubled it to $3.2Bn by June. OpenAI also launched GPT-4 in March 2023 which was multimodal and also new ways of prompting like taking a System message. This was actually intended for enterprise and developer usage leading to the increased revenue numbers.
We had earlier written in detail about the Generative AI landscape globally and how OpenAI’s groundbreaking launch and ChatGPT adoption impacted the tech industry in general.
Google launches Gemini
Google, far from conceding defeat, has quietly and strategically rebuilt its AI capabilities, culminating in the release of Gemini in December 2023 with Nano, Pro and Ultra models. Unlike Bard, Gemini was developed from the ground up as a multimodal AI model, capable of understanding and generating text, images, audio, and video.
Google proudly claimed that Gemini Ultra beat GPT-4 on all tests and even outperformed human experts on MMLU (massive multitask language understanding), achieving a score of 90.0% compared to human expert performance of 89.8%. But it drew a lot of backlash around its manipulative marketing about the demo video being edited and the methodology they used to benchmark against GPT-4. MMLU is a very important benchmark in LLM ranking. All the models are ranked here. GPT-4’s 86.4% beat Gemini Ultra’s 83.7% in an apples to apples comparison.
But even amidst all this, Gemini was praised as it had access to internet (latest information) and worked much better across languages and modes (audio, image) while GPT-4 was trained only till April ‘23.
Gemini’s Rise and OpenAI’s GPT-4 Turbo & GPT-4o AI models
OpenAI released GPT-4 Turbo in November last year with a 128K context token window, 4x that of gpt-4-32k , the largest available till then. While Google followed up with Gemini 1.5 Flash and 1.5 Pro in February 2024 with a 1M context token window and later to 2M in June.
Context is what any LLM uses to keep track of the input prompt , the output it generates and the subsequent inputs provided. It measures context in tokens. A large context token window is required when you want the LLM to read or understand a large amount of data like summarizing a book. Rule of thumb is to consider 4 characters as 1 token. For example, the Steve Jobs biography has ~200,000 words or 250k tokens considering an avg of 5 characters per word.
Why context window is important is because it allows the model to capture more relationships in any data or document that you provide. The most common use case being just retrieval of information from large datasets like legal or scientific queries.
OpenAI followed up with GPT-4o(omni) in May 2024 which was 2x faster and 50% cheaper than GPT-4 Turbo. GPT-4o’s latest August version currently ranks at the top of LMSYS Chatbot Arena outperforming even the latest experimental Gemini 1.5 Pro versions. (that was until the o1 model)
While GPT-4o is clearly beating Gemini in logical reasoning and code generation tasks, Gemini has a better understanding of languages, and that shines in its greater creativity. Also Gemini has superior image and audio input processing as it sits on top of the Chatbot Arena for vision.
Google’s Cloud Advantage
Google Cloud’s revenue grew to $10.35B in Q2 2024, up ~30% from last year. This was led by strong adoption of its GenAI products, especially for enterprises. It signed a deal with Oracle, similar to what Microsoft has, allowing Vertex AI customers to leverage Gen AI capabilities more natively.
Google is focussed on making enterprise-ready GenAI as indicated by its Vertex updates in June 2024 and briefings of Thomas Kurian, Google Cloud CEO in his update. Mentioning several big customers like Uber, Snap and Moody’s, the key updates include –
- Ability to ground the models with google search data and third-party data from Moody’s and Thomson Reuters. This helps with more factuality in the model’s responses leading to better accuracy. Also allows companies to control their brand voice and customer experience. This is what Google calls grounding in “enterprise truth”.
- Higher 2M context token window along with context caching that reduces the cost of input. This is especially important for large context tokens reducing the cost of input.
- Aggressive pricing – Gemini 1.5 Flash is 4x cheaper than the base ChatGPT with larger contexts and better performance.
- Open Platform – It allows customers to use third party models like Anthropic’s Claude and Mistral on Google Cloud. In addition, it has partnered with Accenture, BCG, Cognizant, Deloitte, HCLTech, KPMG, McKinsey, PwC, and Wipro that has spurred thousands of successful projects.
Google is addressing real-life use cases that make a product go from pilot to production. Grounding solved an essential pain point for Enterprises to adopt GenAi products while caching will reduce costs in the long-term. WIth Gemini being integrated more deeply into Google Workspace and Google Cloud, it has the immense opportunity to lead the GenAI adoption of its existing customers.
Along with Gemini, Google also launched its AI-powered research assistant NotebookLM, that has now reached 1M MAU, and is being widely shared.
OpenAI’s September Updates
As we were writing this article, OpenAI released a new o1 model with human-like reasoning and planning. It was trained with reinforcement learning and before answering any question, it pauses and thinks before generating a response [Coding Demo]. This allows it to consider multiple approaches, refine its chain of thought and divide the task into multiple smaller steps with feedback. It could even generate a complete video game in one go.
It blew GPT-4o out of the water. It ranked 89%ile on Codeforces competitive coding questions ( organization (11%ile for gpt-4o). It was 83.3% (v/s 13.4%) accurate for math olympiad questions. It even beat human-experts in the PhD level questions benchmark scoring 78% compared to 69.7% for humans and 56.1% for gpt-4o.
OpenAI admits that although o1 is far superior when it comes to logical reasoning heavy tasks, it’s not much better in language tasks. This is still significant though. Since much of the progress till now has been language-driven resulting in chatbots and assistants that can converse but get a lot of facts all wrong. You might have noticed that if you chat with an LLM and say that its response is wrong, it will almost always agree. This is because it does not have strong attachment to the truth or even some confidence backing its response. All that LLMs have done is memorize all the data they have been fed with and try to find patterns to answer queries in natural language.
However with o1, since it allows for reasoning, the model is better equipped to form connections among the data and reason its way to a conclusion.
With this, OpenAI has once again set the bar high. Although this is great progress for having an all-encompassing AI point of view, it is not ready for widespread adoption. For starters, it is really expensive. o1-preview is $15 per 1 million input tokens, and $60 per 1 million output tokens. That is 3x and 4x compared to GPT-4o itself. And it’s not even worth comparing to Gemini.
OpenAI’s fundraise and struggles
While OpenAI is set to close its new $6.5B funding round, and even has investors ready for another round in 2025, it is struggling to transition from its roots in non-profit AI research.
OpenAI’s CTO Mina Murati, announced she will exit the company soon. This comes in the wake of the company preparing to turn into a for-profit company with a 7% equity stake directly for Sam Altman for the first time. She was one of the highest in command, even taking over the operation during Sam Altman’s brief hiatus in November last year.
Mina Murati joins more than 20 OpenAI researchers, executives and co-founders who have quit in the past year. Co-founder John Schulman left in August to join Anthropic. Ilya Sutskever, co-founder and chief scientist, resigned in May over dilution of the company’s mission and launched a new company Safe Superintelligence with $1B from the same investors as OpenAI. Greg Brockman, the co-founder in whose living room OpenAI was born, is on leave till the end of the year, although he is expected to return.
Ever since Sam Altman returned, there have been tensions brewing related to the conflict between OpenAI’s mission to develop AI for the public good and the pressure to release revenue generating products to fight off its AI rivals and keep investors happy.
For instance, researchers were given only 9 days for safety testing of GPT-4o, just to launch it in May, ahead of Google’s conference. Lots of employees worked 20 hour days to meet the deadline, but later it was found the model faltered on a few safety parameters. The rush to deploy was part of a pattern that affected technical leaders like Murati and other researchers.
Closing remarks
While OpenAI and Google are seen as the two biggest companies here, there’s a number of other companies building use-case specific AI models.
Anthropic released Claude 3.5 Sonnet in June 2024 that has taken code generation to new heights. Its accuracy, efficiency, and near-flawless execution have set a new standard in the industry.
For images, Midjourney has been the most popular model for quite a while. It is still not available via API which restricts its enterprise adoption. Black Forest Labs announced itself with its FLUX image models in August 2024. It also powers Grok’s Text to image capability. Grok is a language model by X owned by Elon Musk. There are several other models like Adobe Firefly, OpenAI DALL-E 3, Google’s Imagen and also applications like Leonardo (acquired by Canva) which use fine-tuned Stable Diffusion models.
Similarly there are several AI Video models, most notably Kling AI by Kuaishou (TikTok rival in China) [Demo] which is touted to be the best until now. Others include Runway, Pika, Luma Labs, and CogVideo (University of Tsinghua in Beijing). While OpenAI released a demo of Sora in February 2024, there has been no further news on that. Google also launched its Video model , Veo in May 2024, but it was much inferior compared to even Sora and has so far not been very popular.
We should remember that Google is a $2 trillion giant that has a much larger responsibility of catering to its over a billion users and seamlessly integrating AI into its thousands of products. They are the Goliath in this David v/s Goliath story while OpenAI is still a startup albeit a $150B one.
