
Before we begin
In a world obsessed with growth at all costs, you believe in retaining the customers & keeping them engaged to make sure they are here to stay. You should block your calendar for just the right event coming up on 6th October. WebEngage, a SaaS player in the marketing automation space is bringing you EngageMint
Dubbed the “Generative AI Revolution,” this groundbreaking innovation is rewriting the rules of creativity and problem-solving across diverse fields—from art and music to healthcare and engineering. As it imbues machines with the ability to create, innovate, and even “think” in ways previously considered the unique domain of human intelligence, the implications are exhilarating. This post serves as a rich repository of hyperlinks covering how we got here, the emergence of Gen AI startups, and its implications on different industries.
OpenAI released ChatGPT on November 30, 2022. A chatbot that can plan a travel itinerary for you with only ₹20,000 to spare and a small suitcase enough for 5 days. It was a glimpse of what talking to an “Intelligent” computer program could look like. And it went viral, reaching the coveted 100 million users mark in just 2 months.
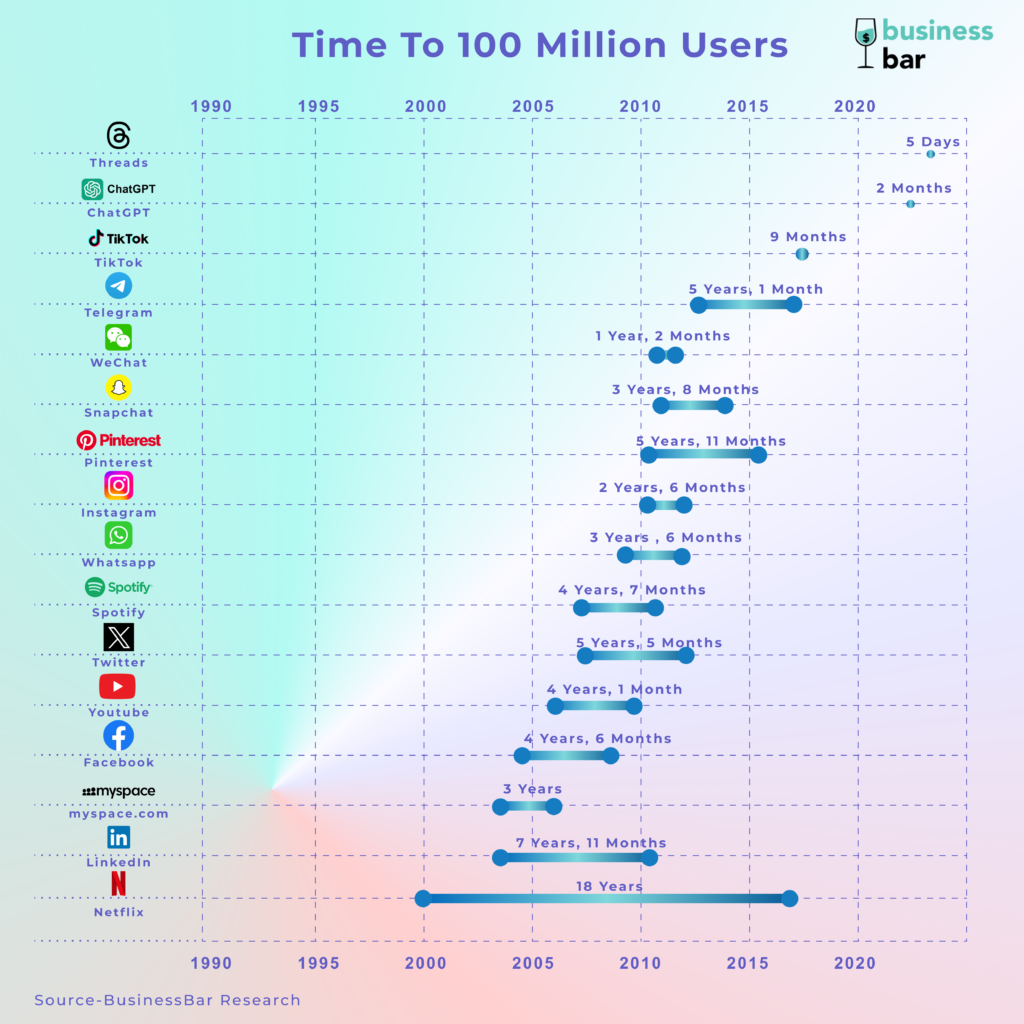
ChatGPT marks its name in history by being the first consumer-facing generative AI application. It can converse in a human-like way and generate a unique response each time (based on the context provided). These 2 factors make it transformational, quite like the dawn of consumer internet apps in the early 2000s. ChatGPT can transcribe an audio or video, provide interactive summaries of podcasts, compose poems on breaking into a house, and even “discover” a faster sorting algorithm. It also generated the first paragraph of this post 🙂.
The seed of development of this line of research was sowed in 2017 with the groundbreaking paper titled “Attention is all you need” which introduced transformers and self-attention. In 2018, researchers at Google published a new language representation model called BERT, which was pre-trained on a large volume of texts using a combination of masked language and next-sentence prediction strategies. At the time, BERT and models built subsequently over it (RoBERTa, DeBERTa, etc.) topped the chart on the GLUE benchmark. (Read more about the history of transformers.)
OpenAI, founded by Sam Altman in 2015, led the effort to build large-scale transformer models, which they called Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs). The first iteration, GPT-1, contained only 117 million parameters and produced text easily identifiable as non-human generated. The release of GPT-3 was a big leap (with 175 billion). The model started producing long texts of prose.
OpenAI, initially a non-profit with the vision of building Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), received backing from Elon Musk and a further $3 billion from Microsoft in 2019.
Post the launch of ChatGPT, Microsoft, realizing the immense world-changing potential of AI and the follow-on effects of it on cloud computing, invested another $10 billion to take its stake in OpenAI to a whopping 49%. Other investors & employees also own 49%, with the original OpenAI Non-Profit retaining just 2%. OpenAI had to convert to a “(capped) for-profit” entity at this point, meaning that the returns to investors and employees are capped. However, the OpenAI Non-Profit still has full control of the capped-profit entity and receives all profit in excess of the defined cap. You can read more about the structure here. Even Sam Altman, their CEO, does not hold any direct equity. He has a small indirect equity from being a Y-Combinator investor who invested a small sum into OpenAI.
Post the blowup of ChatGPT, OpenAI released GPT-4, the successor of GPT-3 (the model on which ChatGPT was first trained), launched in March 2023, passes numerous competitive exams with flying colors, a 90th percentile score on the bar exam, 88th percentile on LSAT, and 99th percentile on GRE (Verbal).
Parallelly brewing was the text-to-image revolution that shares the model architecture in terms of the use of large transformer language models for encoding text for image synthesis. One of the first text-to-image models to capture widespread public attention was DALL-E (also by OpenAI), released in January 2021. By 2022, the output of state-of-the-art models, such as OpenAI’s DALL-E 2, Google Brain’s Imagen, Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney began to approach the quality of real photographs and human-drawn art. Jason Allen’s AI-generated artwork using Midjourney won the Colorado State Fair’s annual art competition (shown below), starting a debate on what comprises art.
From the list above, Midjourney deserves a special mention for taking on giants while being a small, self-funded team of only 11 full-time members (in comparison, Stability AI raised $100M and has roughly 185 members).
The Rise of AI Startups in India
Since the launch of ChatGPT, the number of Generative AI-led SaaS startups in India has more than doubled since 2021 to 60, with $590 million in cumulative funding and $475 million since 2021. Of this, a major chunk (~$240 million) was raised by Gupshup, which had been used to acquire Active.AI and develop its in-house conversational AI to automate customer support. 90% of the total funding, however, went to incumbents (Gupshup, Observe.ai $125M, MadStreetDen $30M, PepperContent $14M), with only ~$50 million invested into companies started since 2021.
Overall, in 2022, AI startups received $3.2 billion in funding out of a total of $25 billion deployed. However, Generative AI is only a fraction of this, as – 1) it is incredibly hard to build a generative AI model, and 2) it has only come into the limelight since the launch of ChatGPT.
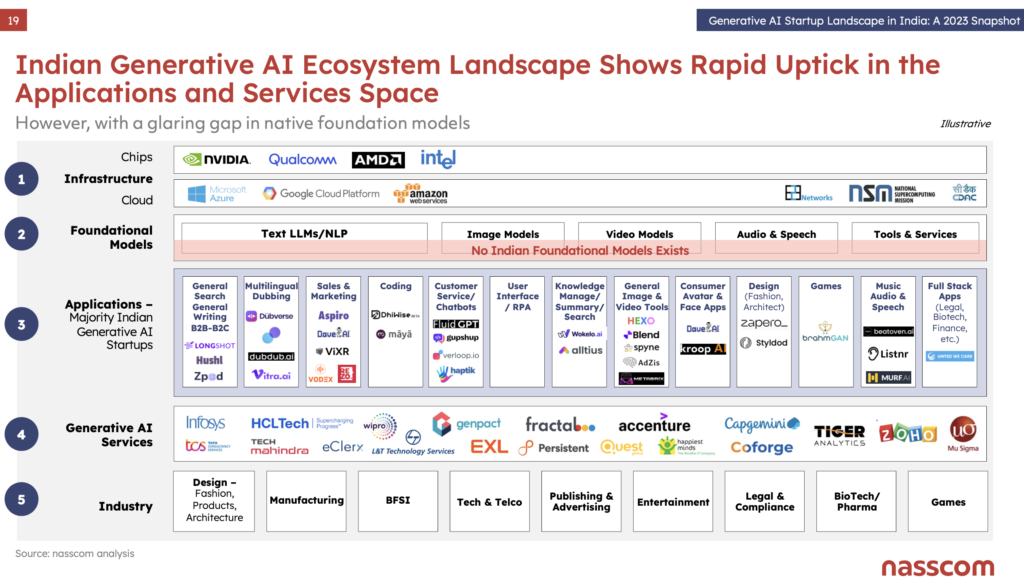
The above graphic is taken out of the “Generative AI Startup Landscape in India” report by Nasscom. There are 2 major takeaways from this –
- Observe the stack on the left side to understand that there are 5 broad layers in the GenAI Ecosystem. It begins with Industry Demand (5) that needs to be served. Then there are Applications, Products(3), and services (4) that can serve this demand with the help of GenAI. For this, they need a foundational AI model, which they can either build in-house or use something like GPT-4, LLaMA (by Meta), BLOOM (by HuggingFace) and many others.
- More importantly, while there are plenty of recognizable names on the Application side, there is a glaring gap as currently there are no AI Foundational Models being built in India. This could be a major loss, especially if we consider the foundational model to be the real innovation and likely to capture all the value in the future.
Sam Altman recently visited India in June 2023, and on being asked if he sees a foundational AI model being built out of India, Altman bluntly replied that one could try, but it is going to be hopeless, but one should try anyway. In other words, it is going to be extremely difficult to build a foundational model in India because it requires money and a certain infrastructure, and those are hard to come by. He added later that the question of doing something that he thinks can’t be done is something that only builders can answer. Rajan Anandan (MD, Peak XV Partners) asked the question, and Anand Mahindra accepted the challenge.
But there’s some truth to this. Over this year, lots of startups have popped up (Glean, Fini, etc. ) that would run the models with the context of private databases of companies, which could then be used to address customer queries, generate FAQs, and or even do advanced data crunching. A single knowledge hub of a company that can answer any and all questions (technical and non-technical). OpenAI launched ChatGPT Enterprise 3 days back (28th August) that did just that.
From engineers troubleshooting bugs to data analysts clustering free-form data, to finance analysts writing tricky spreadsheet formulas—the use cases for ChatGPT Enterprise are plenty. It’s become a true enabler of productivity, with the dependable security and data privacy controls we need.
Danny Wu, Head of AI Products at Canva
And Open AI has plans to do more and take up as much of the pie as it can. And it can do so legitimately since it is the builder and owner of the foundational AI model that has disrupted the market. The presence of the large foundational models for text and images has made it easier for companies to build products directly. In the past, these companies could not have existed due to simply the lack of (artificial) intelligence capabilities. Now, that intelligence can be accessed via APIs costing as little as $0.02 per action.
Facebook has, however, open-sourced its foundational model, LLaMA, along with the configuration needed for anyone to run it on their own. Even if it took hundreds of millions of dollars to make a foundational model, a model, once built, can be finetuned for a few thousand dollars to perform well on a specific task and even outperform a general model like GPT-4.
Ease of building an AI tool/product:
AI Startups raised a mammoth amount of money last year — Inflection AI raised $1.3B to build more personal AI, thus valuing it at $4B. Character.ai raised over $200M Series A to become a unicorn. Mistral AI raised a $113M seed round in just 4 weeks of existence, with just a pitch memo.
Building an AI product has become easier than ever. A whole new job of leveraging the power of these large foundational models has emerged called prompt engineering. Naturally, the question arises on the defensibility of these startups or if they even add as much value as they had been valued at.
Defensibility of Startups
LLMs have made large-scale general data a non-necessity. Small startups can now leverage the power of these models through API and package it into a product. The foundational models themselves are a stronger moat because they cost a lot and take time to build. But they are also not unbeatable because most of the data they were trained on is publicly available (GPT-3 and Stable diffusion were trained on public datasets). Meta went a step ahead and open-sourced their LLaMA 2 model with weights that can be finetuned and self-hosted by companies. The open-source community, too, has made great strides in building smaller models that can match (or even surpass) the capability of ChatGPT or GPT-4 on specific tasks. EleutherIA is a non-profit research institute that evolved from a Discord server and released its GPT Neo family of models with sizes ranging from 125M to 20B parameters. There’s also the BLOOM family of models by HuggingFace, a result of the largest collaboration of AI researchers worldwide. With 176 billion parameters, BLOOM can generate text in 46 languages.
One of the interesting arguments around this was actually from Chamath Palihapitiya, of Facebook fame, who now runs his own venture capital firm, Social Capital. He made the point that once we get to a point where AI is readily available and being used by all major companies, it is going to massively change the mergers and acquisition strategies of these large companies. There is going to be much more value being ascribed to proprietary data (v/s currently the foundational models trained on public data), and companies will get acquired because they will have data that could be good inputs for a larger AI model of the acquirer. You can listen to him here.
As LLMs and AI get more widespread adoption, there could be larger geo-political implications. Take, for example, the recent Digital Personal Data Protection Bill of 2023 that limits the cross-border transfer of data. It could easily be extended to limit the training of models with peculiarities of Indian consumer data or even prevent a pre-trained model from operating on Indian data. Such regulations can also create or destroy moats around Indian startups specifically.
Industries witnessing GenAI revolution
Customer Service: Gen AI has already disrupted the customer service industry. Dukaan laid off 90% of their customer support staff due to their AI bot. They even made a product (bot9.ai) out of it that other startups can use.According to a recent report by Gartner, 70% of organizations are currently exploring Gen AI, with customer experience being the primary focus. Every touchpoint in the customer journey is witnessing automation with more personalized human-like assistance through chat/voice agents. Read BCG’s report on the transformation of customer service through Gen AI.
Media and Entertainment: AI has drastically reduced the cost of producing content. With a subscription of $82/month, you can generate up to 100,000 words per month using Jasper. Jasper raised a $125M Series A at a $1.5B valuation and has fierce competition from Writesonic, Writer, Hypotenuse AI, Quibot, Surfer, etc., in the AI content space. The job of a content writer is witnessing a similar crisis as a customer service agent. While text models and text-to-image models are showing human-like capabilities, video models are still brewing for the next breakthrough, glimpses of which can be seen in the pizza commercial created by Runway using their ML Gen-2 model. The content industry would be transformed by interactive storytelling and personalized, immersive journeys
Search Industry: For the first time in its history, Google stands to be disrupted in search – its crown jewel. ChatGPT transformed the way users interact with the web. Getting a summarized and concise answer is a better UX for users than a list of hyperlinks. Although ChatGPT is lagging far behind in accuracy and coverage, it has started the revolution of moving towards a conversational search. Microsoft, with its acquisition of OpenAI, integrated the technology in Bing. Google, standing at a crossroads with its ad business model at stake, had a setback when its market cap plunged by $100B after its latest chatbot, Bard, shared inaccurate information. It’s a David-vs-Goliath moment with upcoming search startups such as Perplexity AI and Glean (enterprise) quickly integrating the LLMs
Healthcare: LLMs would unlock the creation of structured text from unstructured data (medical reports). Patient communication, such as reminders to checkups, would become conversational and personalized. ChatGPT made news when it diagnosed a life-threatening condition from a user’s post-workout symptoms. Given how critical accuracy is in the medical domain, companies are ramping up to build LLMs for the medical domain (check out Med-PaLM 2 by Google). See McKinsey’s report on tackling the biggest challenges in healthcare using Gen AI
Education and Skill-development: Chegg, an ed-tech company providing online tutoring and homework help, saw its stock fall by nearly 50% after the CEO acknowledged competition from ChatGPT. The traffic on StackOverflow dropped 13.9% in February and 17.7% in March, establishing the supremacy of ChatGPT in not only providing answers to everyday questions but also code snippets.
E-commerce: The experience of e-commerce is going to change with visual search (virtual try-on). Customers would be able to see how the product would appear on them. Google is already making headway by weaving GenAI into its shopping features to take on Amazon. Recommendations would become more personalized and convincing, with explanations provided to users about why a product was suggested.
Gaming Industry: The use of Gen AI accelerates the game development process by creating assets, writing dialogues, and generating levels. Ubisoft unveiled its new AI writing program, Ghostwriter, which aids in crafting phrases spoken by NPC characters. Roblox also launched a similar AI-based tool for its game creators. Read more about different games using Gen AI here
Implication of AI in personal life and future of work
Increased productivity: Knowledge workers would see a substantial increase in their productivity with the adoption of AI tools. Ben’s Bites, a newsletter featuring the latest AI products, has a repository of 8000+ tools. We now have tools for everything — note-taking and writing (Mem, Notion AI), scheduling (Reclaim, Clockwise, Motion), scraping websites (Webscrape AI), creating websites (Framer), creating AI videos (Descript, Runway, Decoherence), meeting assistants (Fireflies.ai, Krisp, Airgram), create slide decks (Beautiful.ai, Decktopus), or even to evaluate your startup pitch (Pitchyouridea.ai). The website Supertools curates 1000s of such tools across categories.
Future of work: A recent paper on the labor market impact of LLMs highlights that 80% of the US workforce would have 10% of their task affected by LLMs. According to McKinsey’s report, around 3% of the global workforce will need to change the occupational category by 2030. Quoting the report,
Occupations made up of physical activities in highly structured environments or in data processing or collection will see declines. Growing occupations will include those with difficult-to-automate activities, such as managers, and those in unpredictable physical environments, such as plumbers.
AI, automation, and the future of work: Ten things to solve for – McKinsey
We tried our best to fit all that we could in this article. For those interested in diving deep into the rabbit hole, we leave you with a ton of articles, blogs and other reads for you to dive into. Cheers! Hope you enjoyed this one.
References / Further Readings
Articles / Reading Lists / Personal Blogs
History of Transformers – https://archive.vn/xAdam
Will LLMs Disrupt Google Search? – https://matt-rickard.com/will-llms-disrupt-google
The New AI Moats – https://matt-rickard.com/the-new-ai-moats
Eight AI Startups Winning the Race for Tech Talent – https://medium.com/lightspeed-venture-partners/eight-ai-startups-winning-the-race-for-tech-talent-571a18b03642
Anti-hype LLM reading list from HackerNews – https://gist.github.com/veekaybee/be375ab33085102f9027853128dc5f0e
Lilian Weng’s learning notes (Team Lead, AI Safety @OpenAI) – https://lilianweng.github.io/
Eugene Yan’s personal blog on LLMs (Senior Applied Scientist @Amazon) – https://eugeneyan.com/
AI reading list by Andreessen Horowitz – https://a16z.com/2023/05/25/ai-canon/
AI reading list by Lightspeed – https://medium.com/lightspeed-venture-partners/what-lightspeed-is-reading-listening-and-thinking-about-ai-b30ad8d24eb6
Emerging Architecture for LLM Applications by Andreessen Horowitz – https://a16z.com/2023/06/20/emerging-architectures-for-llm-applications/
Learn Prompting – https://learnprompting.org/docs/intro
Newsletters
Towards AI (latest research) – https://towardsai.net/
Ben Bites (latest products) – https://bensbites.co/
Market Research
Nasscom Report – Generative AI Startup Landscape in India
Reports by McKinsey –
AI, Automation, and the future of work
Tackling healthcare’s biggest burdens with generative AI
What’s the future of generative AI? An early view in 15 charts
